Ethereum is emerging as one of the most prominent blockchain platforms in the digital asset ecosystem. As millions of investors worldwide continue to pour their resources into cryptocurrencies, a critical security concern has become increasingly apparent: your digital assets are only as secure as the infrastructure that holds them. The fundamental principle that defines blockchain technology—its decentralized, immutable nature—is precisely what makes it the safest environment for your cryptocurrency. Yet countless investors unknowingly compromise this security by storing their assets outside the blockchain’s protective framework.
Recent incidents involving centralized exchanges, custodial services, and third-party platforms have demonstrated a harsh reality that every cryptocurrency holder must understand. When you remove your digital assets from the blockchain’s native security architecture, you expose yourself to vulnerabilities that the technology was specifically designed to eliminate. This comprehensive exploration of cryptocurrency security will reveal why keeping your Ethereum and other digital assets firmly anchored on the blockchain isn’t just a best practice—it’s an absolute necessity for anyone serious about protecting their investment.
Blockchain Security Fundamentals
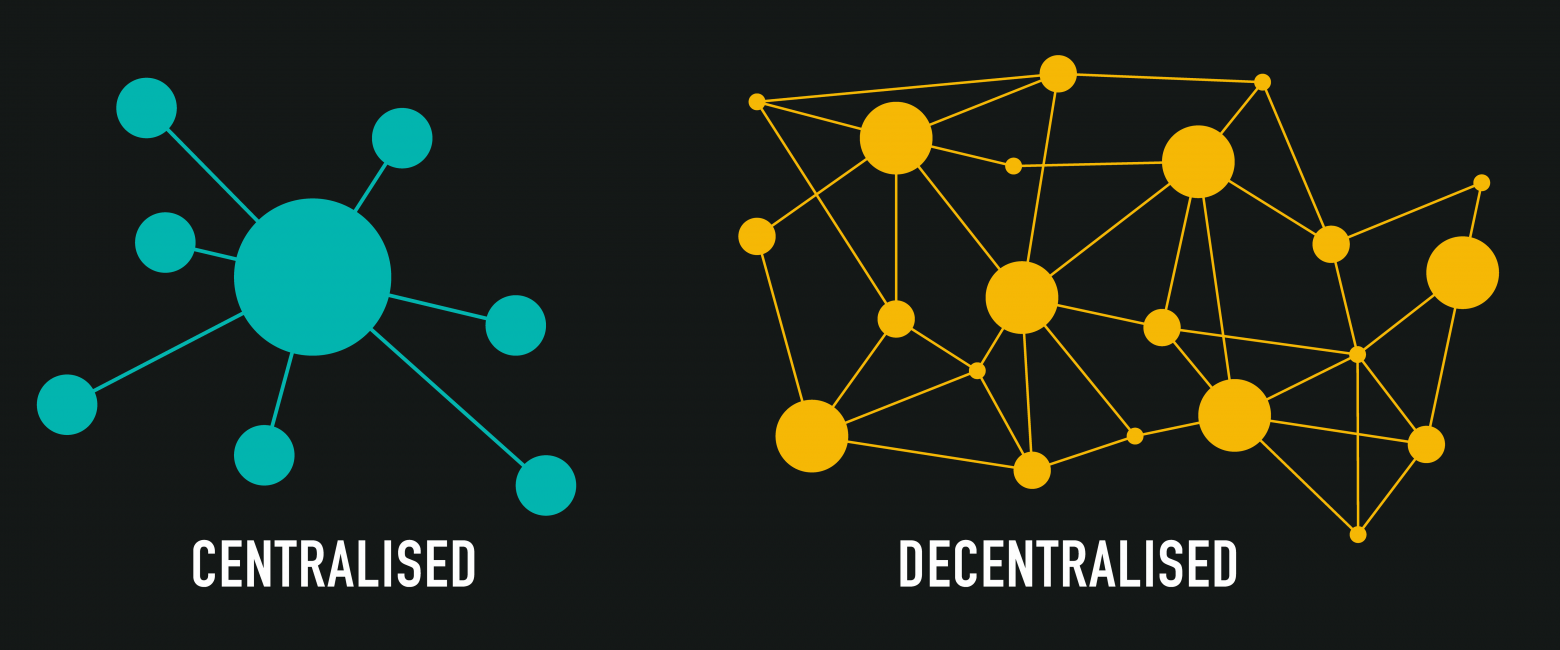
The blockchain represents a revolutionary approach to securing digital information through cryptographic protocols and distributed consensus mechanisms. At its core, Ethereum’s blockchain operates as a decentralized ledger where every transaction becomes permanently recorded across thousands of independent nodes worldwide. This architectural design creates multiple layers of security that make unauthorized alterations virtually impossible without controlling the majority of the network’s computational power.
When your cryptocurrency resides directly on the blockchain, it benefits from the collective security of the entire network. Each block contains a cryptographic hash of the previous block, creating an unbreakable chain of verification that extends back to the genesis block. This structure means that attempting to alter any historical transaction would require recalculating every subsequent block—a computational feat that becomes exponentially more difficult as the blockchain grows longer and the network becomes more distributed.
Smart contracts on Ethereum add another dimension to this security framework. These self-executing agreements operate according to predetermined conditions without requiring intermediaries. When properly audited and implemented, smart contracts eliminate human error and manipulation from the equation, ensuring that your digital assets move only according to the exact parameters you’ve established. This automated trustless system represents the ultimate expression of blockchain security, where code becomes law and mathematical certainty replaces the need for faith in centralized authorities.
The Risks of Centralized Exchange Storage
Centralized cryptocurrency exchanges have become the on-ramp for millions entering the digital asset marketplace, offering user-friendly interfaces and convenient trading platforms. However, these platforms fundamentally contradict the decentralized ethos that makes blockchain technology secure. When you deposit cryptocurrency on an exchange, you’re essentially transferring ownership to the platform’s custodial wallets, where your assets sit alongside those of countless other users in what the industry calls “hot wallets.”
The vulnerability of this arrangement has been demonstrated repeatedly through devastating security breaches. From the infamous Mt. Gox collapse that saw 850,000 Bitcoin disappear to more recent incidents involving major platforms, the pattern remains disturbingly consistent. Centralized exchanges create honey pots that attract sophisticated cybercriminals, state-sponsored hackers, and even internal bad actors. Despite implementing advanced security measures, these platforms cannot match the inherent security of the blockchain itself because they represent single points of failure.
Beyond external threats, centralized exchanges face operational risks that can lock users out of their funds indefinitely. Regulatory actions, bankruptcy proceedings, liquidity crises, and technical failures have all resulted in situations where investors suddenly find themselves unable to access their cryptocurrency. The FTX collapse in 2022 served as a stark reminder that even the most prominent and seemingly trustworthy platforms can implode spectacularly, leaving users fighting for years to recover a fraction of their holdings. These platforms operate under “not your keys, not your coins” conditions, meaning the exchange maintains ultimate control over asset access regardless of what your account balance displays.
Self-Custody and Hardware Wallet Solutions
Taking personal custody of your Ethereum holdings through proper wallet management represents the gold standard for cryptocurrency security. Self-custody means you alone control the private keys that grant access to your blockchain assets, eliminating intermediary risk. This approach aligns perfectly with the blockchain’s design philosophy, where cryptographic proof replaces institutional trust and individuals maintain sovereign control over their wealth.
Hardware wallets provide the most secure method for self-custody by keeping your private keys completely offline in specialized devices designed specifically for cryptocurrency storage. These physical devices generate and store your private keys in isolated environments that never expose them to internet-connected computers, even when signing transactions. Leading hardware wallet manufacturers implement secure element chips similar to those used in passports and credit cards, creating multiple layers of protection against both physical and digital attacks.
The process of using a hardware wallet reinforces the connection between your assets and the blockchain itself. When you need to send Ethereum or interact with decentralized applications, the hardware wallet signs transactions internally before broadcasting them to the network. Your private keys never leave the device, meaning even if the computer you’re using is compromised by malware, your cryptocurrency remains secure. This methodology keeps your assets firmly anchored on the blockchain while giving you complete control over transaction authorization—the perfect balance between security and accessibility.
Software Wallets and Best Security Practices
For users who require more frequent access to their cryptocurrency, software wallets offer a middle ground between exchange custody and hardware wallet security. These applications can run on your computer or smartphone, providing convenient access to your blockchain assets while maintaining control of your private keys. However, software wallets require diligent security practices because they operate on internet-connected devices vulnerable to various attack vectors.
Implementing proper security protocols transforms software wallets into reasonably secure solutions for everyday cryptocurrency management. This begins with choosing reputable, open-source wallet software that has undergone extensive security audits and maintains active development communities. Your device’s overall security posture directly impacts your wallet’s safety, making regular operating system updates, antivirus protection, and cautious browsing habits essential components of cryptocurrency security best practices.
Multi-signature configurations add security layer by requiring multiple private keys to authorize transactions. This approach can involve using different devices, sharing authorization with trusted parties, or creating time-locked conditions that prevent rapid asset movement. Multi-signature wallets particularly benefit businesses and individuals managing substantial cryptocurrency holdings, as they eliminate single points of failure while maintaining assets on the blockchain itself. The flexibility of modern wallet solutions allows users to tailor security measures to their specific risk tolerance and usage patterns without sacrificing the fundamental protection that blockchain technology provides.
Decentralized Finance and Smart Contract Interactions
The explosive growth of decentralized finance (DeFi) has created new opportunities for earning yields and accessing financial services without traditional intermediaries. However, DeFi also introduces unique security considerations that every Ethereum user must understand before depositing assets into protocols. Unlike centralized exchanges, DeFi platforms operate entirely through smart contracts on the blockchain, meaning your assets technically remain on-chain even while participating in these protocols.
Despite maintaining blockchain custody, DeFi interactions carry distinct risks that differ from simply holding cryptocurrency in your personal wallet. Smart contract vulnerabilities, whether from coding errors or intentional backdoors, can expose your assets to exploitation. The DeFi ecosystem has witnessed numerous incidents where protocol flaws allowed attackers to drain millions of dollars in seconds. Before depositing assets into any DeFi protocol, thorough research into the project’s security audits, time in operation, total value locked, and development team reputation becomes absolutely critical.
Governance token systems and liquidity pools introduce additional complexity to DeFi security. Participating in these mechanisms often requires permitting smart contracts to access your tokens, creating potential vulnerabilities if the contract contains exploitable code. The concept of “rug pulls,” where project developers suddenly drain liquidity pools and disappear, represents another threat vector unique to the DeFi space. Understanding these risks doesn’t mean avoiding DeFi entirely, but rather approaching these opportunities with the same cautious diligence you would apply to any significant financial decision while recognizing that maintaining assets on the blockchain through reputable protocols still offers superior security compared to centralized alternatives.
The Importance of Private Key Management
Your private keys represent the ultimate authority over your blockchain assets—they are the cryptographic proof of ownership that the network recognizes as legitimate. Understanding that private key security directly determines your cryptocurrency safety cannot be overstated. These alphanumeric strings might look like meaningless character sequences, but they contain the mathematical relationship that proves your right to move specific assets recorded on the blockchain.
The blockchain’s immutable nature means that lost private keys result in permanently inaccessible funds. Unlike traditional banking systems, where forgotten passwords can be reset through customer service, blockchain transactions cannot be reversed or overridden by any central authority. This characteristic, while representing blockchain’s greatest strength against censorship and seizure, also places absolute responsibility on users to safeguard their keys. Countless stories exist of individuals losing access to significant cryptocurrency holdings because of inadequate backup procedures or catastrophic key management failures.
Creating robust backup systems for your private keys or seed phrases requires balancing accessibility with security. Writing down seed phrases on paper and storing them in secure physical locations—such as fireproof safes or bank deposit boxes—protects against digital threats while maintaining recovery options. More sophisticated users might implement Shamir’s Secret Sharing, which splits seed phrases into multiple parts requiring a threshold number to reconstruct. Metal seed phrase storage devices offer protection against fire and water damage, addressing physical threats that could destroy paper backups. Whatever method you choose, remember that these backups represent direct access to your blockchain assets, making their security equivalent to protecting physical gold or cash.
Recognizing Common Security Threats
The cryptocurrency ecosystem attracts malicious actors employing increasingly sophisticated techniques to separate users from their assets. Phishing attacks represent one of the most prevalent threats, where criminals create convincing replicas of legitimate wallet websites or applications to trick users into revealing their private keys or seed phrases. These scams have become remarkably sophisticated, sometimes involving fake browser extensions, fraudulent mobile applications, or spoofed emails that appear indistinguishable from legitimate communications.
Social engineering attacks exploit human psychology rather than technical vulnerabilities, manipulating users into voluntarily compromising their security. These schemes might involve impersonating customer support representatives, creating artificial urgency around account security issues, or offering too-good-to-be-true investment opportunities requiring immediate private key disclosure. The anonymity and irreversibility of blockchain transactions make cryptocurrency particularly attractive to social engineers because successful scams result in immediate, untraceable theft with no possibility of chargebacks or intervention.
Clipboard hijacking malware represents a more technical but equally dangerous threat where malicious software monitors your computer’s clipboard for cryptocurrency addresses and replaces them with attacker-controlled addresses. This attack exploits the common practice of copying and pasting long blockchain addresses, potentially resulting in funds being sent to criminals instead of intended recipients. Protecting against these diverse threats requires maintaining constant vigilance, verifying all transaction details before confirmation, and understanding that legitimate services never request your private keys or seed phrases under any circumstances. The blockchain’s security framework can only protect you if you maintain control of your authentication credentials and follow established security protocols.
The Future of Cryptocurrency Security
As blockchain technology matures, new security innovations continue to emerge to address existing vulnerabilities while maintaining the decentralized principles that make the technology revolutionary. Layer-2 solutions on Ethereum, such as Optimism and Arbitrum, provide enhanced transaction throughput without compromising the base layer’s security guarantees. These scaling solutions inherit Ethereum’s security model while offering reduced transaction costs and faster confirmation times, making blockchain usage more practical for everyday transactions.
Account abstraction represents another significant advancement that could dramatically improve user experience without sacrificing security. This approach allows smart contract wallets to implement customizable security features like social recovery mechanisms, spending limits, and multi-factor authentication while maintaining full self-custody. The technology enables more forgiving security models where losing a single device doesn’t necessarily mean losing access to your assets, addressing one of the biggest barriers preventing mainstream blockchain adoption.
Biometric authentication integration, quantum-resistant cryptography, and improved hardware security modules all promise to strengthen cryptocurrency security as the industry evolves. However, these innovations will remain meaningless if users continue storing assets off-chain through custodial services. The fundamental lesson persists regardless of technological advancement: your cryptocurrency achieves maximum security when it remains on the blockchain under your direct control through proper self-custody practices. As the industry progresses, the gap between on-chain security and the risks associated with centralized custody will likely widen rather than narrow.
Conclusion
The blockchain represents humanity’s most sophisticated approach to securing digital assets through mathematics, cryptography, and distributed consensus rather than institutional trust. Ethereum and other blockchain networks offer unprecedented security guarantees when users properly engage with the technology according to its design principles. Your cryptocurrency achieves maximum protection when it remains on the blockchain under your direct control through self-custody solutions, whether hardware wallets, properly secured software wallets, or carefully vetted DeFi protocols.
The convenience offered by centralized exchanges and custodial services creates an illusion of security while actually introducing the exact vulnerabilities that blockchain technology was invented to eliminate. Every major exchange hack, platform bankruptcy, and regulatory seizure reinforces the unchanging truth: not your keys, not your coins. Understanding this principle and taking action to secure your private keys represents the single most important step any cryptocurrency holder can take to protect their investment.
As the digital asset ecosystem continues expanding, the responsibility for security remains firmly in individual hands. The blockchain provides the tools and framework for absolute financial sovereignty, but only users who embrace proper security practices will truly benefit from this revolutionary technology. Your crypto isn’t safe outside the blockchain—make sure yours stays where it belongs.
FAQs
Q: What is the safest way to store Ethereum long-term?
The safest method for long-term Ethereum storage involves using a reputable hardware wallet like Ledger or Trezor, which keeps your private keys completely offline in a secure element chip. Always purchase hardware wallets directly from manufacturers to avoid tampering, and create multiple secure backups of your seed phrase stored in separate physical locations. For maximum security, consider implementing a multi-signature setup requiring multiple devices to authorize transactions, and never enter your seed phrase into any digital device or website.
Q: Can I lose my cryptocurrency if the exchange I use gets hacked?
Yes, absolutely. When you store cryptocurrency on an exchange, you don’t actually control those assets—the exchange does. If hackers breach the exchange’s security or the platform experiences bankruptcy, technical failures, or regulatory actions, your funds can become inaccessible or lost entirely. History has shown that even the largest, most trusted exchanges can suffer catastrophic failures. The only way to guarantee protection against exchange-related losses is by maintaining self-custody of your private keys through personal wallets.
Q: Is it difficult to manage my own cryptocurrency wallet?
While self-custody requires more responsibility than leaving assets on an exchange, modern wallet solutions have become increasingly user-friendly. Hardware wallets offer intuitive interfaces with clear instructions, and the initial learning curve pays dividends through dramatically improved security. The process primarily involves purchasing a hardware wallet, initializing it, securely backing up your seed phrase, and sending your cryptocurrency to the wallet’s address. Most users become comfortable with the process within an hour, and the peace of mind knowing your assets are truly secure makes the minimal effort worthwhile.
Q: What happens if I lose my hardware wallet?
Losing your hardware wallet doesn’t mean losing your cryptocurrency, provided you’ve created proper backups of your seed phrase. The seed phrase serves as a master backup that can regenerate all your private keys on a replacement device. Simply purchase a new hardware wallet, select the recovery option during setup, and enter your seed phrase to restore complete access to your blockchain assets. This is why securing your seed phrase backups is more critical than protecting the physical device itself.
Q: Are DeFi protocols safer than centralized exchanges?
DeFi protocols offer different security characteristics than centralized exchanges. Your assets remain on the blockchain when using DeFi, eliminating custody risk, but they become subject to smart contract vulnerabilities and protocol-specific risks. Well-established DeFi platforms with extensive security audits, long operational histories, and significant total value locked generally offer better security than custodial exchanges. However, newer or unaudited protocols can be extremely risky. The key is thoroughly researching any DeFi platform before depositing assets, understanding that blockchain custody through reputable protocols remains fundamentally more secure than trusting centralized intermediaries.


![Bitcoin vs Altcoins Who Wins the Breakout [2026 Analysis]](https://spearcrypto.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/01/Bitcoin-vs-Altcoins-Who-Wins-the-Breakout-2026-Analysis-390x220.jpg)